Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide, a major cause of cancer deaths, and deadly if left untreated. This article will help you learn more about “cervical cancer”.
What is cervical cancer? What are its causes? Are treatments and prevention methods, such as HPV vaccination or screening, effective?
Learn more about cervical cancer
- What is cervical cancer?
- Causes of cervical cancer
- Symptoms of cervical cancer

- How to Test for Cervical Cancer?

- Is cervical cancer curable?
- Treatment for cervical cancer
- Prevention

What is cervical cancer?

Most cervical cancer patients report engaging early sexual activity (especially under 17) or having husbands or multiple sexual partners (or a partner with many partners).![]()

Cervical cancer is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) strains. This virus is transmitted through sexual intercourse that causes abrasions to the skin or mucous membranes of the genitals, allowing the virus to enter the cervix. This leads to changes in the cervical tissue or cells, resulting in chronic inflammation and eventually cancer.
Causes of cervical cancer
Causes and risk factors of cervical cancer are as follows.

- Transmission through sexual intercourse
- Age: Often found in women over 40
- having multiple sexual partners significantly increases the risk of exposure to the HPV
- Smoking
- Having multiple children
- Immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV)
- Never having had a pelvic exam or cervical screening
- Never receiving the HPV vaccine
- History of sexually transmitted infections
Symptoms of cervical cancer
Warning signs and symptoms indicating a higher risk of cervical cancer that require urgent medical attention are as follows.
- Bleeding after sex, douching, or pelvic exams
- Vaginal bleeding not related to your period
- Vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Increased, foul-smelling, or bloody vaginal discharge
- Unexplained lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Sores or lumps found in the cervix.
How to Test for Cervical Cancer?

Cervical cancer can be detected through screening. Regular cervical cancer screening is crucial for early detection because precancerous changes and early cancer often have no symptoms. During this asymptomatic period, cervical cells may have already metastasized into cancer, making treatment difficult and life-threatening.
“Regular cervical cancer screening is crucial for early detection of abnormal changes, for early treatment that significantly boosts cure rates”
Recommended screening tests include Pap Smear, ThinPrep, and HPV DNA tests.
Is cervical cancer curable?
Cervical cancer is highly curable when found in the early stages. Regular cervical cancer screening is the best method for early detection of abnormal cell changes that lead to cervical cancer.
Treatment for Cervical Cancer
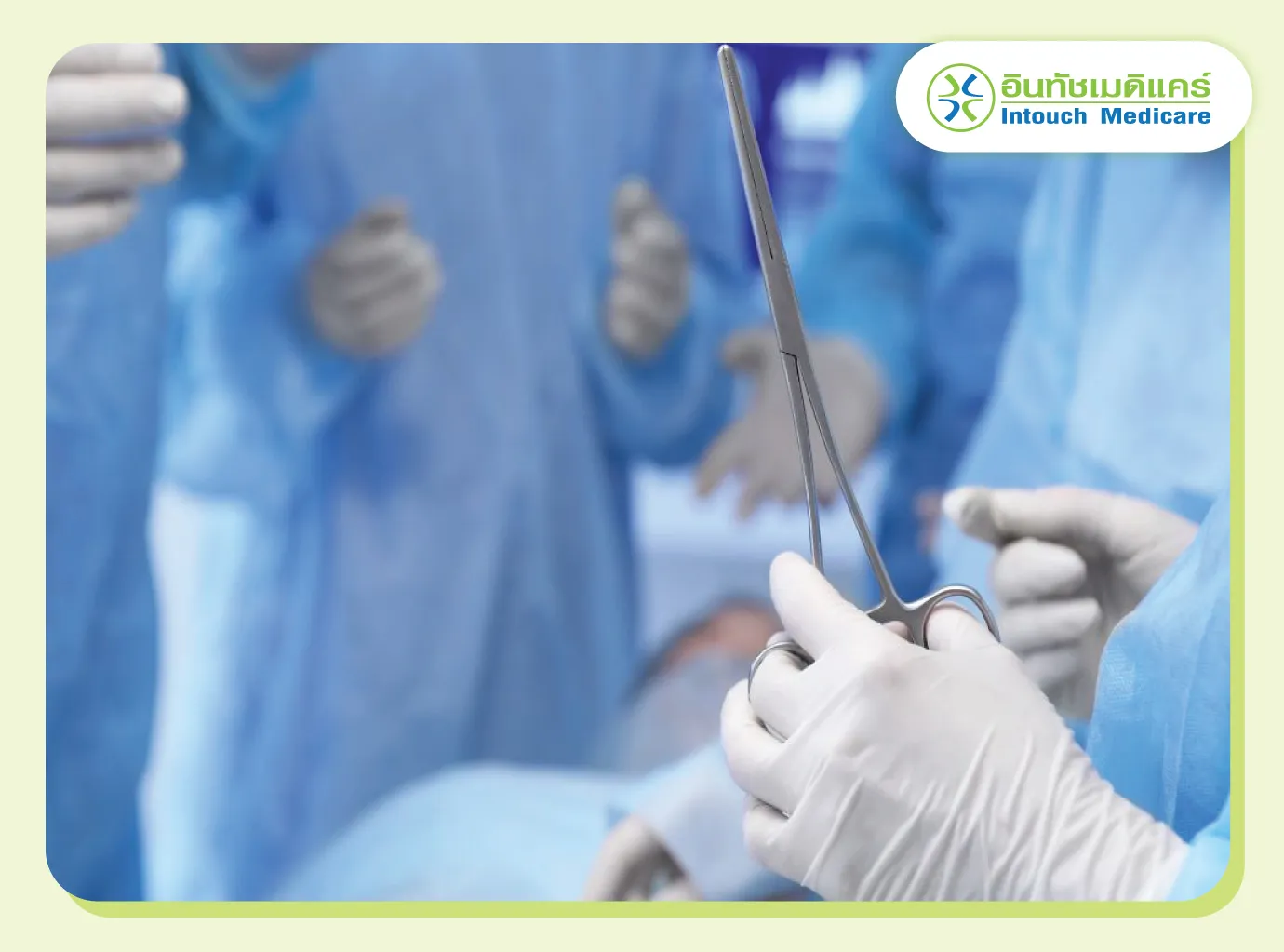
Surgery
Surgery is a key for early-stage cervical cancer, often a radical hysterectomy (uterus, cervix, upper vagina, surrounding tissues, pelvic lymph nodes) for most cases, but a less extensive simple hysterectomy (removal of the cervix and uterus) can suffice for tiny, very early tumors.
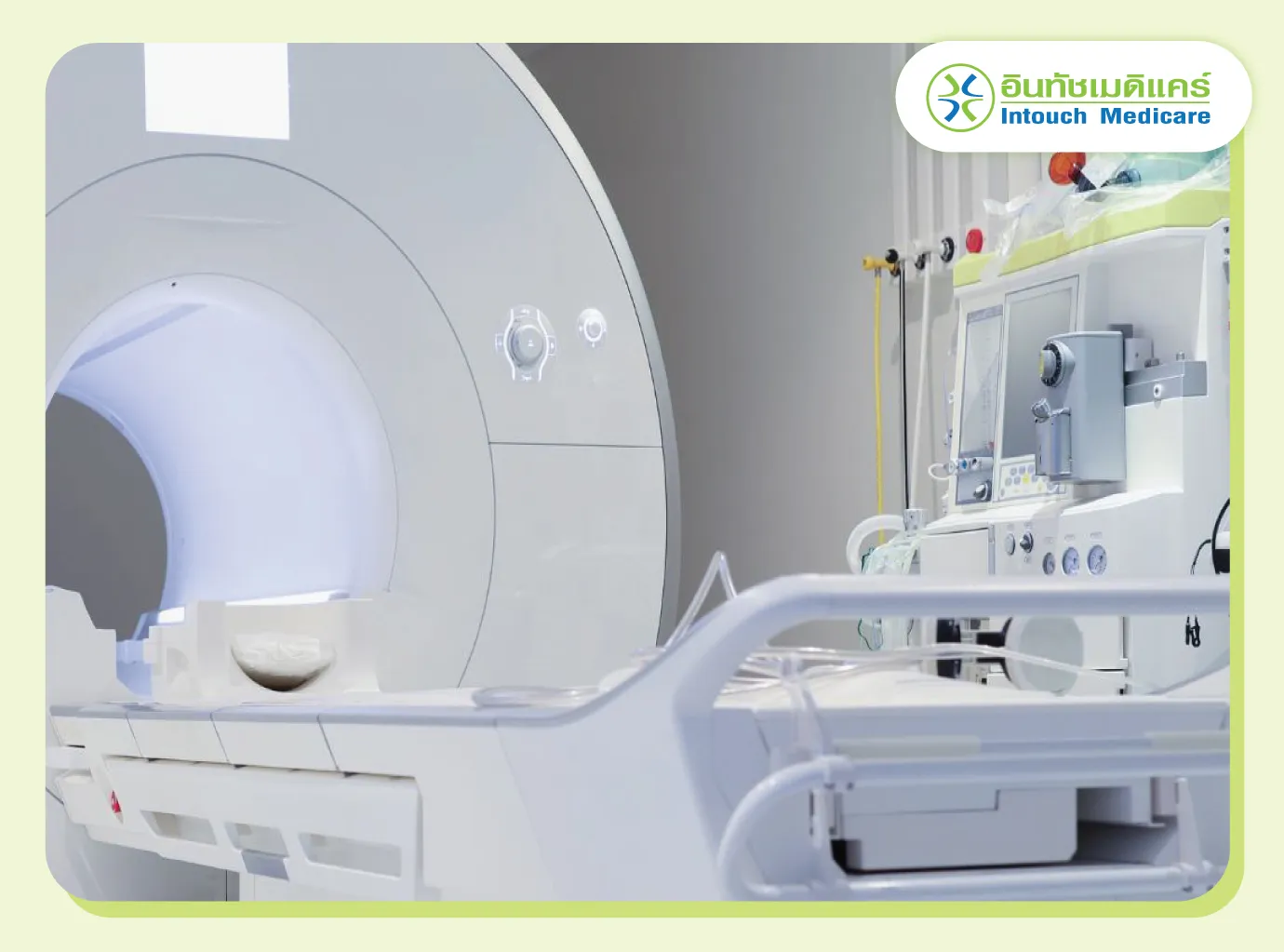
Radiation
For locally advanced cervical cancer, a combination of chemotherapy with external beam radiation is standard treatment, with brachytherapy often added to boost the dose right to the tumor by delivering high-dose radiation close to the cancer using applicators placed in the vagina or uterus for short periods.
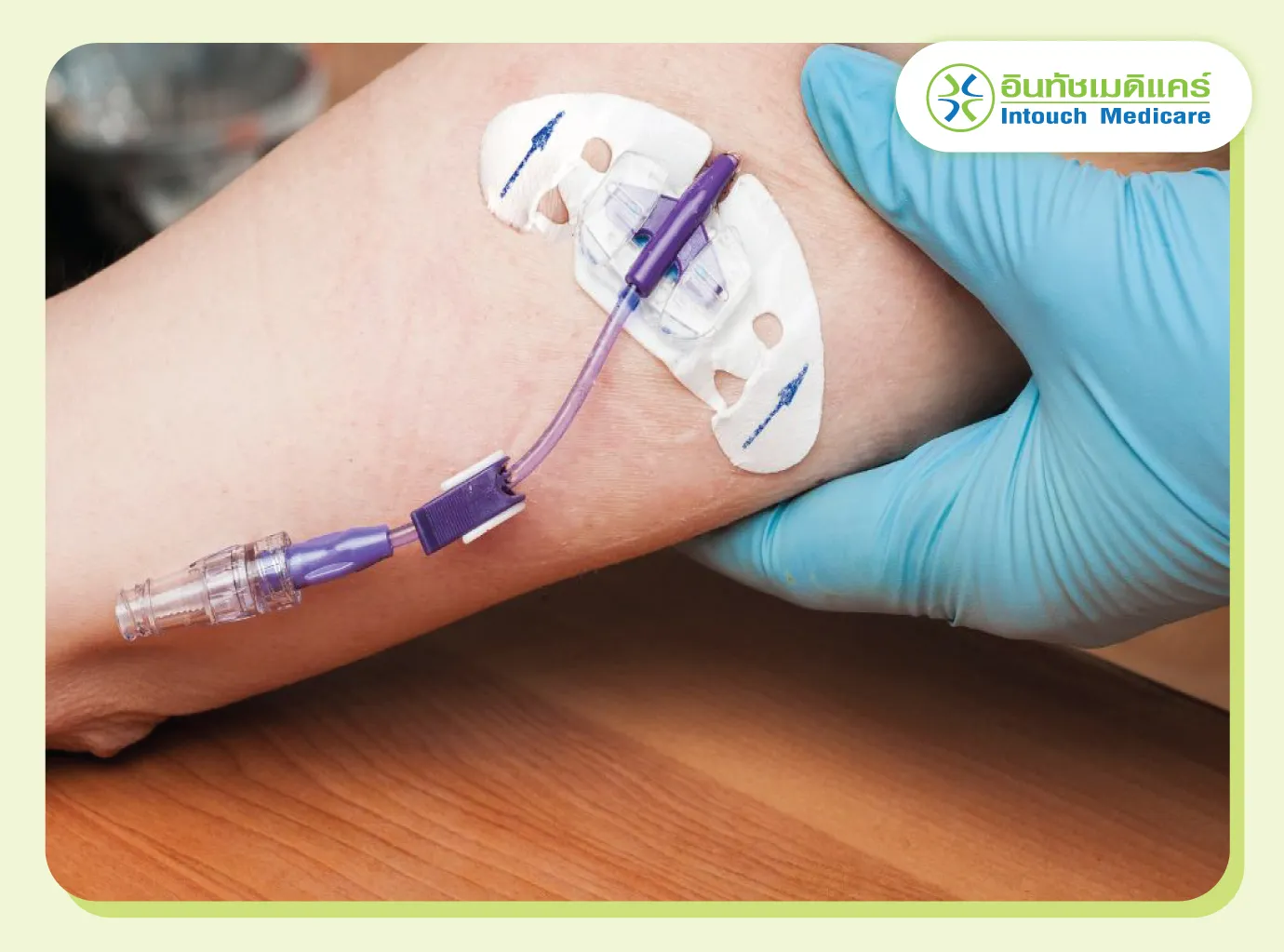
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a treatment for widespread cancer (metastasis) or and relapses.
- A combination of low dose chemotherapy with radiation is used for locally advanced cervical cancer,
- Chemotherapy is the primary treatment for metastatic cervical cancer,
Prevention
HPV Vaccination
- HPV vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent infections from Human Papillomavirus. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) confirms HPV vaccine is highly 100effective (near 100% in trials) in preventing cervical cancer caused by the high-risk HPV strains, especially when given before infection.
- HPV vaccine is highly effective at preventing the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infections that cause vaginal cancer, vulvar cancer, throat cancer, and genital warts.
- Over 140 countries worldwide have incorporated HPV vaccination into their national health programs for prevention.
Cervical cancer screening
- Pap Smear is a screening method for detecting abnormal cervical cells including “precancerous changes” and “early cancers, often before they’re visible”.
- ThinPrep Pap Test is a cervical cancer screening method that involves collecting cells into a vial of liquid.
- HPV DNA Test detects cancer-causing HPV strains in cervical/vaginal lining, detecting infection early, even before precancerous changes or symptoms.
Regular Exercise
Research confirms that completely inactive women face significantly higher cervical cancer risk (around 2.5 times) compared to exercisers. This is due to the fact that a weak immune system leads to frequent sickness, while inactivity disrupts sleep, and insufficient sleep further compromises immunity, creating a vicious loop of getting sick and feeling tired.
Safe Sex Practices
Safe sex practices include
- Use condoms

- Get regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections
- Avoid having multiple sexual partners

- Avoid becoming sexually active at a young age
Stop Smoking
Smoking significantly raises the risk for many cancers, including lung, liver, esophageal, and cervical cancer, by introducing carcinogens that damage DNA and weaken the immune system.
Cervical cancer is one of the most frightening diagnoses to give to a woman but highly preventable and manageable through the HPV vaccine, regular screening for early precancer detection, and timely treatment. While they don’t offer 100% prevention, these proactive steps are far better than waiting for symptoms, which often appear late.
If you are interested in getting cervical cancer screening or HPV vaccination at IntouchMedicare, please chat with us via LINE Chat for inquiries or appointments.
References
- Asst. Prof. Puchong Likittanasombut, M.D., Cervical Cancer
- American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, Smoking and Cervical Cancer
- Global partners cheer progress towards eliminating cervical cancer and underline challenges, World Heath Organization
Interesting Articles
- Pelvic examination and cervical cancer screening
- Cervical Cancer Vaccine (HPV Vaccine) – Is It Necessary?
For more info and make appointment

Intouchmedicareclinic
Medical Clinic
![]() Latest edit : 15/12/2025
Latest edit : 15/12/2025
![]() Images may be used without prior permission exclusively for educational or informational purposes, as long as proper credit is given to intouchmedicare.com
Images may be used without prior permission exclusively for educational or informational purposes, as long as proper credit is given to intouchmedicare.com


 MM
MM




